 Shifting Graphs Up/Down Left/Right
Shifting Graphs Up/Down Left/Right
|
|
|
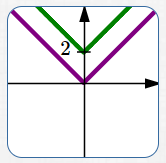
$y = f(x)$ $y = f(x) + 2$ Up $2$ |
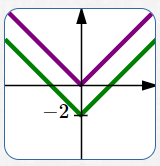
$y = f(x)$ $y = f(x) - 2$ Down $2$ |
|
Movements up and down change the $y$-values of points. Transformations that affect the $y$-values are intuitive. For example, to move up $\,2\,,$ you add $\,2\,$ to the previous $y$-value. |
|
|
|
|
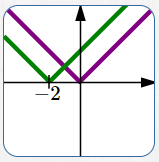
$y = f(x)$ $y = f(x+2)\,$ Left $2$ |
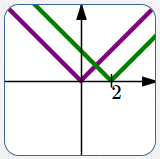
$y = f(x)$ $y = f(x-2)\,$ Right $2$ |
|
Movements left and right change the $x$-values of points. Transformations that affect the $x$-values are counter-intuitive. For example, to move left $\,2\,,$ you replace every $\,x\,$ by $\,x+2\,,$ not $\,x-2\,.$ |
|
The lesson Graphing Tools: Vertical and Horizontal Translations in the Algebra II curriculum gives a thorough discussion of shifting graphs up/down left/right. The key concepts are repeated here.
The exercises in this lesson duplicate those in Graphing Tools: Vertical and Horizontal Translations.
-
Points on the graph of $\,y=f(x)\,$ are of the form $\,\bigl(x,f(x)\bigr)\,.$
Points on the graph of $\,y=f(x)+3\,$ are of the form $\,\bigl(x,f(x)+3\bigr)\,.$
Thus, the graph of $\,y=f(x)+3\,$ is the same as the graph of $\,y=f(x)\,,$ shifted UP three units.
- Transformations involving $\,y\,$ work the way you would expect them to work—they are intuitive.
-
Here is the thought process you should use when you are given the graph of $\,y=f(x)\,$ and asked about the graph of $\,y=f(x)+3\,$:
Interpretation of new equation:
$$ \begin{gather} \overset{\text{the new y-values}}{\overbrace{ \strut\ \ y\ \ }} \overset{\text{are}}{\overbrace{ \strut\ \ =\ \ }} \overset{\text{the previous y-values}}{\overbrace{ \strut f(x)}} \overset{\ \ \text{with 3 added to them}}{\overbrace{ \strut\ \ + 3\ \ }} \end{gather} $$Summary of Vertical Translations
Let $\,p\,$ be a positive number.
Start with the equation $\,\color{purple}{y=f(x)}\,.$ Adding $\,\color{green}{p}\,$ to the previous $\color{green}{y}$-values gives the new equation $\,\color{green}{y=f(x)+p}\,.$ This shifts the graph UP $\,\color{green}{p}\,$ units.
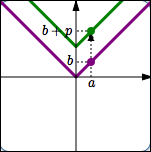
A point $\,\color{purple}{(a,b)}\,$ on the graph of $\,\color{purple}{y=f(x)}\,$ moves to a point $\,\color{green}{(a,b+p)}\,$ on the graph of $\,\color{green}{y=f(x)+p}\,.$
Additionally:
Start with the equation $\,\color{purple}{y=f(x)}\,.$ Subtracting $\,\color{green}{p}\,$ from the previous $\color{green}{y}$-values gives the new equation $\,\color{green}{y=f(x)-p}\,.$ This shifts the graph DOWN $\,\color{green}{p}\,$ units.
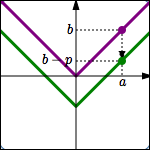
A point $\,\color{purple}{(a,b)}\,$ on the graph of $\,\color{purple}{y=f(x)}\,$ moves to a point $\,\color{green}{(a,b-p)}\,$ on the graph of $\,\color{green}{y=f(x)-p}\,.$
This transformation type (shifting up and down) is formally called vertical translation.
Ideas Regarding Horizontal Translations (Moving Left/Right)
-
Points on the graph of $\,y=f(x)\,$ are of the form $\,\bigl(x,f(x)\bigr)\,.$
Points on the graph of $\,y=f(x+3)\,$ are of the form $\,\bigl(x,f(x+3)\bigr)\,.$
-
How can we locate these desired points $\,\bigl(x,f(x+3)\bigr)\,$?
First, go to the point $\,\color{red}{P\bigl(x+3\,,\,f(x+3)\bigr)}\,$ on the graph of $\,\color{red}{y=f(x)}\,.$
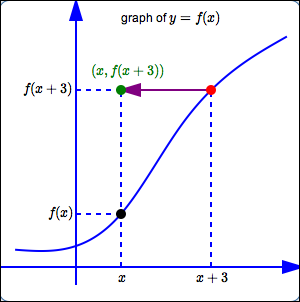
This point has the $y$-value that we want, but it has the wrong $x$-value.
Move this point $\,\color{purple}{3}\,$ units to the left. Thus, the $y$-value stays the same, but the $x$-value is decreased by $\,3\,.$ This gives the desired point $\,\color{green}{\bigl(x,f(x+3)\bigr)}\,.$
Thus, the graph of $\,y=f(x+3)\,$ is the same as the graph of $\,y=f(x)\,,$ shifted LEFT three units.
Thus, replacing $\,x\,$ by $\,x+3\,$ moved the graph LEFT (not right, as might have been expected!)
-
Transformations involving $\,x\,$ do NOT work the way you would expect them to work! They are counter-intuitive—they are against your intuition.
-
Here is the thought process you should use when you are given the graph of $\,y=f(x)\,$ and asked about the graph of $\,y=f(x+3)\,$:
$$ \begin{align} \text{original equation:} &\quad y=f(x)\cr \text{new equation:} &\quad y=f(x+3) \end{align} $$$$ \begin{gather} \text{Interpretation of new equation:}\cr\cr y = f( \overset{\text{replace $x$ by $x+3$}}{\overbrace{ x+3}} ) \end{gather} $$Replacing every $\,x\,$ by $\,x+3\,$ in an equation moves the graph $\,3\,$ units TO THE LEFT.
Summary of Horizontal Translations
Let $\,p\,$ be a positive number.
Start with the equation $\,\color{purple}{y=f(x)}\,.$ Replace every $\,\color{green}{x}\,$ by $\,\color{green}{x+p}\,$ to give the new equation $\,\color{green}{y=f(x+p)}\,.$ This shifts the graph LEFT $\,\color{green}{p}\,$ units.
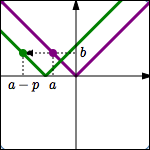
A point $\,\color{purple}{(a,b)}\,$ on the graph of $\,\color{purple}{y=f(x)}\,$ moves to a point $\,\color{green}{(a-p,b)}\,$ on the graph of $\,\color{green}{y=f(x+p)}\,.$
Additionally:
Start with the equation $\,\color{purple}{y=f(x)}\,.$ Replace every $\,\color{green}{x}\,$ by $\,\color{green}{x-p}\,$ to give the new equation $\,\color{green}{y=f(x-p)}\,.$ This shifts the graph RIGHT $\,\color{green}{p}\,$ units.
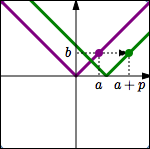
A point $\,\color{purple}{(a,b)}\,$ on the graph of $\,\color{purple}{y=f(x)}\,$ moves to a point $\,\color{green}{(a+p,b)}\,$ on the graph of $\,\color{green}{y=f(x-p)}\,.$
This transformation type (shifting left and right) is formally called horizontal translation.Different Words Used to Talk About Transformations Involving $\,y\,$ and $\,x\,$
Notice that different words are used when talking about transformations involving $\,y\,,$ and transformations involving $\,x\,.$
For transformations involving $\,y\,$ (that is, transformations that change the $y$-values of the points), we say:
DO THIS to the previous $y$-value
For transformations involving $\,x\,$ (that is, transformations that change the $x$-values of the points), we say:
REPLACE the previous $x$-values by $\ldots$
Make Sure You See the Difference!
Vertical translations:
Going from
$\,y=f(x)\,$
to
$\,y = f(x) \pm c\,$
Horizontal translations:
Going from
$\,y = f(x)\,$
to
$\,y = f(x\pm c)\,$
Make sure you see the difference between (say) $\,y = f(x) + 3\,$ and $\,y = f(x+3)\,$!
In the case of $\,y = f(x) + 3\,,$ the $\,3\,$ is ‘on the outside’: we're dropping $\,x\,$ in the $\,f\,$ box, getting the corresponding output, and then adding $\,3\,$ to it. This is a vertical translation.
In the case of $\,y = f(x + 3)\,,$ the $\,3\,$ is ‘on the inside’: we're adding $\,3\,$ to $\,x\,$ before dropping it into the $\,f\,$ box. This is a horizontal translation.
Examples
Concept Practice
Note: There are lots of questions like this:
‘Start with $\,y = f(x)\,.$ Move UP $\,2\,.$ What is the new equation?’
Here is the same question, stated more precisely:
‘Start with the graph of $\,y=f(x)\,.$ Move this graph UP $\,2\,.$ What is the equation of the new graph?’
All the ‘graphs’ are implicit in the problem statements. (When something is implicit then it's understood to be there, even though you can't see it.)