 Reflecting About Axes, and the Absolute Value Transformation
Reflecting About Axes, and the Absolute Value Transformation
|
|
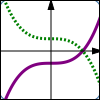
$y = f(x)$ $y = -f(x)$ Reflect about the $x$-axis |
|
|
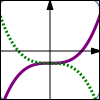
$y = f(x)$ $y = f(-x)$ Reflect about the $y$-axis |
|
|
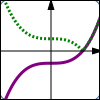
$y = f(x)$ $y = |f(x)|$ The absolute value transformation: any part of the graph above the $x$-axis stays the same; any part of the graph below the $x$-axis ‘flips up’ |
The lesson Graphing Tools: Reflections and the Absolute Value Transformation in the Algebra II curriculum gives a thorough discussion of reflecting about the $x$-axis and the $y$-axis, and the absolute value transformation. The key concepts are repeated here.
The exercises in this lesson duplicate those in Graphing Tools: Reflections and the Absolute Value Transformation.
Ideas Regarding Reflecting About the $x$-axis
-
Points on the graph of $\,y=f(x)\,$ are of the form $\,\bigl(x,f(x)\bigr)\,.$
Points on the graph of $\,y=-f(x)\,$ are of the form $\,\bigl(x,-f(x)\bigr)\,.$
Thus, the graph of $\,y=-f(x)\,$ is found by taking the graph of $\,y=f(x)\,,$ and multiplying the $y$-values by $\,-1\,.$ This reflects the graph about the $x$-axis.
- Transformations involving $\,y\,$ work the way you would expect them to work—they are intuitive.
-
Here is the thought process you should use when you are given the graph of $\,y=f(x)\,$ and asked about the graph of $\,y=-f(x)\,$:
$$ \begin{align} \cssId{s23}{\text{original equation:}} &\quad \cssId{s24}{y=f(x)}\cr \cssId{s25}{\text{new equation:}} &\quad \cssId{s26}{y=-f(x)} \end{align} $$ $$ \begin{gather} \cssId{s27}{\text{Interpretation of new equation:}}\cr\cr \overset{\cssId{s29}{\text{the new $y$-values}}}{\overbrace{ \strut\ \ \cssId{s28}{y}\ \ }} \overset{\cssId{s31}{\text{are}}}{\overbrace{ \strut\ \ \cssId{s30}{=}\ \ }} \overset{\cssId{s33}{\ \text{$-1$ times}\ }}{\overbrace{ \strut \ \ \cssId{s32}{-}\ \ }} \overset{\cssId{s35}{\ \text{the previous $y$-values}}}{\overbrace{ \strut\ \ \cssId{s34}{f(x)}\ \ }} \end{gather} $$ -
In reflection about the $x$-axis, a point $\,(a,b)\,$ on the graph of $\,y=f(x)\,$ moves to a point $\,(a,-b)\,$ on the graph of $\,y=-f(x)\,.$
Ideas Regarding Reflecting About the $y$-axis
-
Points on the graph of $\,y=f(x)\,$ are of the form $\,\bigl(x,f(x)\bigr)\,.$
Points on the graph of $\,y=f(-x)\,$ are of the form $\,\bigl(x,f(-x)\bigr)\,.$
-
How can we locate these desired points $\,\bigl(x,f(-x)\bigr)\,$?
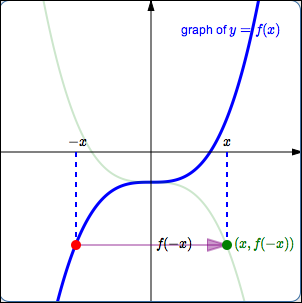
Pick a value of $\,x\,.$ First, go to the point $\,\color{red}{\bigl(-x\,,\,f(-x)\bigr)}\,$ on the graph of $\,\color{red}{y=f(x)}\,.$
This point has the $y$-value that we want, but it has the wrong $x$-value. The $x$-value of this point is $\,-x\,,$ but the desired $x$-value is just $\,x\,.$
Thus, the current $\color{purple}{x}$-value must be multiplied by $\color{purple}{-1}\,$; that is, each $\color{purple}{x}$-value must be sent to its opposite. The $\color{purple}{y}$-value remains the same. This causes the point to reflect about the $y$-axis, and gives the desired point $\,\color{green}{\bigl(x,f(-x)\bigr)}\,.$
Thus, the graph of $\,y=f(-x)\,$ is the same as the graph of $\,y=f(x)\,,$ except that it has been reflected about the $y$-axis.
-
Here is the thought process you should use when you are given the graph of $\,y=f(x)\,$ and asked about the graph of $\,y=f(-x)\,$:
$$ \begin{align} \cssId{s54}{\text{original equation:}} &\quad \cssId{s55}{y=f(x)}\cr \cssId{s56}{\text{new equation:}} &\quad \cssId{s57}{y=f(-x)} \end{align} $$ $$ \begin{gather} \cssId{s58}{\text{Interpretation of new equation:}}\cr\cr \cssId{s59}{y = f( \overset{\text{replace $x$ by $-x$}}{\overbrace{ \ \ -x\ \ }} )} \end{gather} $$Replacing every $\,x\,$ by $\,-x\,$ in an equation causes the graph to be reflected about the $y$-axis.
-
In reflection about the $y$-axis, a point $\,(a,b)\,$ on the graph of $\,y=f(x)\,$ moves to a point $\,(-a,b)\,$ on the graph of $\,y=f(-x)\,.$
Ideas Regarding the Absolute Value Transformation
-
Points on the graph of $\,y=f(x)\,$ are of the form $\,\bigl(x,f(x)\bigr)\,.$
Points on the graph of $\,y=|f(x)|\,$ are of the form $\,\bigl(x,|f(x)|\bigr)\,.$
-
Thus, the graph of $\,y=|f(x)|\,$ is found by taking the graph of $\,y=f(x)\,$ and taking the absolute value of the $y$-values.
Points with positive $y$-values stay the same, since the absolute value of a positive number is itself. That is, points above the $x$-axis don't change.
Points with $\,y=0\,$ stay the same, since the absolute value of zero is itself. That is, points on the $x$-axis don't change.
Points with negative $y$-values will change, since taking the absolute value of a negative number makes it positive. That is, any point below the $x$-axis reflects about the $x$-axis.
These actions are summarized by saying that ‘any part of the graph below the $x$-axis flips up’.
-
Here is the thought process you should use when you are given the graph of $\,y=f(x)\,$ and asked about the graph of $\,y=|f(x)|\,$:
$$ \begin{align} \cssId{s80}{\text{original equation:}} &\quad \cssId{s81}{y=f(x)}\cr \cssId{s82}{\text{new equation:}} &\quad \cssId{s83}{y=|f(x)|} \end{align} $$ $$ \begin{gather} \cssId{s84}{\text{Interpretation of new equation:}}\cr\cr \overset{\cssId{s86}{\text{the new $y$-values}}}{\overbrace{ \strut\ \cssId{s85}{y}\ }} \overset{\cssId{s88}{\text{are}}}{\overbrace{ \strut\ \cssId{s87}{=}\ }} \overset{\cssId{s90}{\text{the absolute value of the previous $y$-values}}}{\overbrace{ \strut\ \cssId{s89}{|f(x)|}}} \end{gather} $$ -
In the absolute value transformation, a point $\,(a,b)\,$ on the graph of $\,y=f(x)\,$ moves to a point $\,(a,|b|)\,$ on the graph of $\,y=|f(x)|\,.$
Summary
Reflecting about the
$x$-axis:
going from $\,y = f(x)\,$ to $\,y = -f(x)$
Reflecting about the
$y$-axis:
going from $\,y = f(x)\,$ to $\,y = f(-x)$
Absolute value transformation:
going from $\,y = f(x)\,$ to $\,y = |f(x)|$
Any part of the graph on or above the
$x$-axis stays the same;
any part of the graph below the
$x$-axis flips up.
Make Sure You See the Difference!
Make sure you see the difference between $\,y = -f(x)\,$ and $\,y = f(-x)\,$!
In the case of $\,y = -f(x)\,,$ the minus sign is ‘on the outside’: we're dropping $\,x\,$ in the $\,f\,$ box, getting the corresponding output, and then multiplying by $\,-1\,.$ This is reflection about the $x$-axis.
In the case of $\,y = f(-x)\,,$ the minus sign is ‘on the inside’: we're multiplying $\,x\,$ by $\,-1\,$ before dropping it into the $\,f\,$ box. This is reflection about the $y$-axis.